Eczema, a skin ailment impacting individuals of every age, results in redness, itchiness, and discomfort. While it’s a common condition, it comes in various forms, each with its own set of triggers and symptoms. Understanding the different types of eczema along with eczema itching medicine and learning how to manage itching can greatly improve your quality of life. In this article, we will identify the various types of eczema and provide effective strategies to soothe itching.
What Is Eczema?
Eczema, or dermatitis, is a persistent skin ailment known for skin inflammation, redness, itchiness, and, at times, the development of dry, scaly patches on the skin’s surface. It can affect people of all ages, from infants to adults, and it often has genetic and environmental factors as triggers. It can result from a combination of genetic predisposition, a compromised skin barrier, immune system dysfunction, and environmental factors like allergens and irritants. Managing eczema typically involves moisturizing the skin; avoiding triggers can alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Types of Eczema
To determine your specific eczema type, closely observe your skin and any associated symptoms. Take note of when and where flare-ups occur, as well as any patterns or triggers that seem to exacerbate the condition. While there are several types of eczema, the most common is atopic dermatitis.
Let’s explore the different types of eczema to gain a better understanding of this condition.
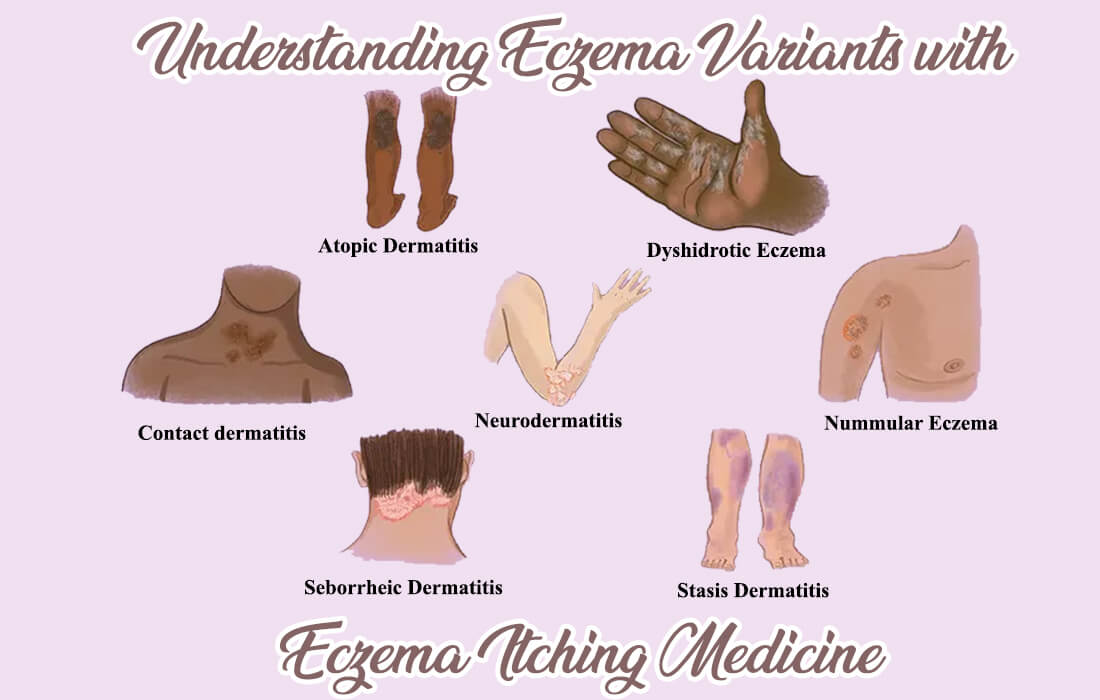
1. Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, the most common variation of eczema, frequently co-occurs with a familial background of allergies or asthma. It typically appears in childhood and can continue into adulthood. Common symptoms include red, itchy skin that may develop into dry and scaly patches. The itching can be intense, leading to frequent scratching and potential skin infections.
2. Contact dermatitis
The occurrence of contact dermatitis is the result of skin contact with an irritant or allergen. It can be classified into two categories: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. Irritant contact dermatitis is the more common type and arises due to contact with abrasive agents like strong soaps, detergents, or chemicals. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when an individual has an allergic reaction to specific substances like nickel, latex, or certain plants like poison ivy.
3. Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema, also known as pompholyx eczema, primarily affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It presents with tiny, pruritic blisters that can be rather uncomfortable. This type of eczema tends to be more common in warm weather and can be triggered by factors like stress or contact with certain metals, so it’s essential to acquire medicine for eczema on hands.
4. Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema presents with round or coin-like patches of inflamed skin. These patches provoke severe itching and are commonly situated on the arms, legs, and torso. It is important to note that nummular eczema is not typically associated with allergies. Instead, its common causes include dry skin, temperature shifts, or physical injuries to the skin.
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis, a form of eczema, predominantly impacts the scalp, face, and chest. It is often associated with flaky, greasy scales and can cause redness and itching. This condition is commonly named “cradle cap” in infants and called dandruff in adults.
6. Neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis, recognized as Lichen simplex chronicus, presents as a persistent skin condition that causes thickened, scaly patches and intense itching. It often occurs in response to repetitive scratching or rubbing of the skin, leading to a cycle of itching and skin damage. Stress, anxiety, or underlying skin conditions can trigger this condition. Treatment typically involves managing the itching, reducing stress, and addressing any contributing factors to break the itch-scratch cycle.
7. Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis typically occurs in individuals with poor circulation, often in the lower legs and ankles. It is associated with symptoms such as redness, swelling, and itchy skin. This type of eczema can lead to the development of venous ulcers, which are open sores that require eczema itching medicine.
Different Ways for Soothing Eczema Itching
Itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema, and it can be incredibly uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are various strategies you can use to soothe itching and manage your eczema effectively.
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping your skin well-hydrated is key to managing eczema. Use a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer and apply it to your skin immediately after bathing. It helps lock in moisture and prevents your skin from drying out.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that exacerbate your eczema can go a long way in reducing itching. Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, allergens, and certain foods. Pay attention to what aggravates your symptoms and take steps to minimize exposure.
- Choose the Right Clothing: Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing made from natural fibres like cotton can help reduce friction and irritation on your skin. Avoid tight-fitting garments, wool, and synthetic fabrics that can trap heat and moisture.
- Use Lukewarm Water: Hot water can wash away your skin’s natural oils, making eczema symptoms more severe. Instead, opt for lukewarm water when bathing or showering, and limit your bathing time to 10-15 minutes to prevent over-drying your skin.
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser when washing your skin. Avoid harsh soaps and scrubbing, as they can irritate your skin further. After showering, use a soft towel to pat your skin dry, avoiding rough rubbing.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms, making it essential to embrace effective stress management methods. Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga are effective in stress reduction and can provide relief from itching.
Conclusion
Eczema may pose challenges, but by employing effective strategies and proper management, you can successfully mitigate its symptoms and relieve itching. One crucial step is determining the specific type of eczema affecting you. Ensure you follow your skincare routine consistently, avoid triggers, and seek eczema treatment medicine when needed. With patience, you can make significant improvements to the health and appearance of your skin.