Diabetes is a persistent health issue that afflicts a considerable number of individuals. This condition arises when your blood sugar or glucose levels are consistently above normal. Managing blood sugar control is crucial for people with diabetes to lead healthy lives. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into different types of diabetes, including the medicine for blood sugar control and explore effective ways to manage blood sugar levels.
Understanding Diabetes Types
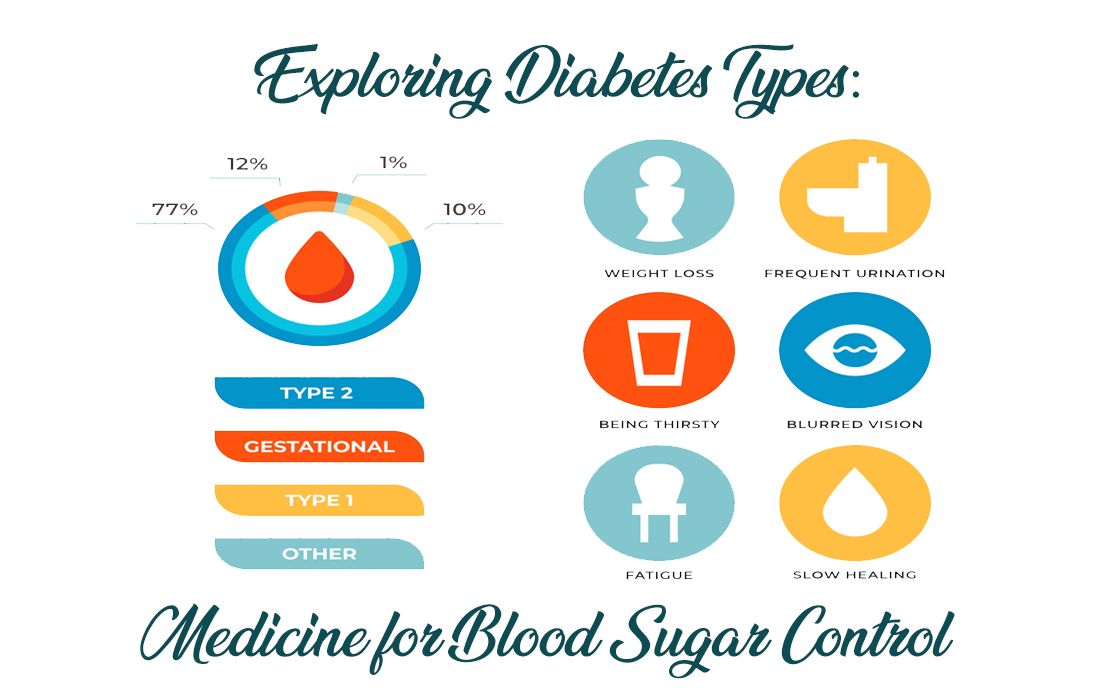
Diabetes manifests in diverse ways, with each type having unique underlying causes, distinguishing features, and techniques for managing the condition.
a) Type 1 Diabetes:
- An autoimmune response identifies type 1 diabetes and is frequently referred to as insulin-dependent diabetes. In this type of diabetes, the immune system erroneously singles out and targets the beta cells that manufacture insulin in the pancreas, causing a decline in insulin production.
- Type 1 diabetes commonly initiates during childhood or adolescence, though its onset can occur at any stage of life.
- People living with Type 1 diabetes rely on daily insulin injections or utilize insulin pumps to supplement their bodies’ deficient insulin production. Insulin plays an essential role in facilitating the body’s utilization of glucose, which is the vital source of energy obtained from sugar circulating in the blood.
- While lifestyle factors can affect blood sugar control, they are not the primary cause of Type 1 diabetes. However, it is essential to underscore that a wholesome diet, best medicine for diabetes type 1 and consistent exercise are paramount in controlling blood sugar levels for those with type 1 diabetes.
b) Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is the prevailing form of diabetes, encompassing the majority of diagnosed cases. This condition arises when the body’s response to insulin diminishes, and the pancreas cannot generate adequate insulin to offset this reduced response.
- Type 2 diabetes commonly manifests in adulthood, although it can also emerge during a young age. Lifestyle factors, notably an unhealthy diet and insufficient physical activity are significantly linked to its development.
- Type 2 diabetes management often requires individuals to change their lifestyle, such as adopting a balanced diet and actively participating in physical activities. In some cases, medicine for diabetes type 2 may be necessary to control blood sugar levels. All these changes can help improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
c) Gestational Diabetes:
- When a woman is pregnant, gestational diabetes can occur because her body cannot produce enough insulin to meet her increased needs.
- It is specific to pregnancy and typically goes away after childbirth. On the other hand, women diagnosed with gestational diabetes are at a heightened likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes at a later stage in life.
- Managing this form of diabetes mostly entails dietary modifications, and in certain situations, the incorporation of insulin treatment is necessary. Proper management is crucial to ensuring the health of both the mother and the developing baby.
- The likelihood of developing gestational diabetes increases if there is a history of diabetes in the family if the pregnant woman is dealing with obesity, or if her age exceeds 25 years during pregnancy.
d) Prediabetes:
- Prediabetes is when the blood sugar exceeds the normal range but does not reach the threshold for a Type 2 diabetes diagnosis. It acts as an early alert, signalling an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Prediabetes can develop at any age and often precedes the onset of Type 2 diabetes.
- Prediabetes risk factors include excess weight or obesity, a family history of diabetes, and a lifestyle characterized by physical inactivity.
- Fortunately, prediabetes is reversible. By adjusting your lifestyle, which encompasses shedding pounds and adopting a balanced diet, you can take proactive steps to lower your blood sugar levels and mitigate the chances of developing Type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that regardless of the type of diabetes, effective management is crucial to prevent complications and maintain good health. Managing diabetes requires a dual focus on monitoring blood sugar levels and making wise lifestyle decisions.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose, is critical to our body’s internal environment. It serves as the predominant energy source for our cells and is essential for maintaining our overall health. The body retains a precise balance of blood sugar levels to ensure a continuous and stable energy supply to our cells. However, when this delicate balance is disrupted, it can lead to health issues, particularly diabetes. Understanding blood sugar, its regulation, and how to keep it within a healthy range is vital for maintaining optimal well-being and preventing complications related to conditions like diabetes.
Whether you’re contending with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, there are practical techniques available to help you manage and stabilize your sugar level within healthy limits. Let’s explore these straightforward tactics:
1. Healthy Eating
- Prioritize a diet that strikes a balance by including whole grains, lean proteins, an array of fruits and vegetables, and also fats that are beneficial for your well-being.
- Make an effort to eat both less sugary and processed foods.
- Be mindful of serving sizes to prevent excessive consumption.
2. Regular Exercise
- Enhance your body’s ability to use insulin effectively by including activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling in your regular schedule.
- Aim for at least moderate-intensity exercise per week.
3. Medications or Insulin
- Take your medicine for blood sugar control or insulin as directed by your physician.
- Make it a routine to monitor your blood glucose levels to confirm they stay within the limits.
4. Stress Management
- Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels—practice stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
5. Get Enough Sleep
- Aim for quality sleep per night, as poor sleep can disrupt blood sugar control.
6. Monitor Carbohydrate Intake
- Pay attention to your carbohydrate intake and discover how different foods can have varying effects on your blood glucose levels.
7. Stay Hydrated
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush excess sugar from your bloodstream.
Conclusion
Effective diabetes management and stable blood sugar levels are of utmost importance. It’s necessary to emphasize that diabetes is a complex condition, and its management can vary greatly from person to person. There are various types of diabetes, each with its own causes, risk factors, and also the management strategies. Regular monitoring, dedication to a healthy lifestyle and seeking proper medicine for blood sugar control are key steps to effectively managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. With these effective tactics, you can enjoy a fulfilling life while managing and stabilizing your blood sugar levels successfully.