Image by pch.vector on Freepik
Psoriasis, a persistent skin ailment, afflicts numerous individuals, manifesting as red, scaly skin patches prone to itching and discomfort. For individuals living with psoriasis, Ayurvedic medicine for psoriasis effectively addresses symptoms and improves their overall quality of life. This blog examines the diverse forms of psoriasis and offers insights into successful management.
An Introduction to Psoriasis
Psoriasis, characterized by the excessive and fast-paced growth of skin cells, is a persistent autoimmune skin condition. In individuals with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly triggers skin cells to reproduce at an accelerated rate, forming red, raised, and often itchy patches or plaques covered with silvery-white scales. These patches can appear on various body parts, including the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and nails. Psoriasis involves a combination of genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. It is a non-contagious condition, and its severity can vary from mild, with only a few small patches, to severe, affecting large areas of the skin.
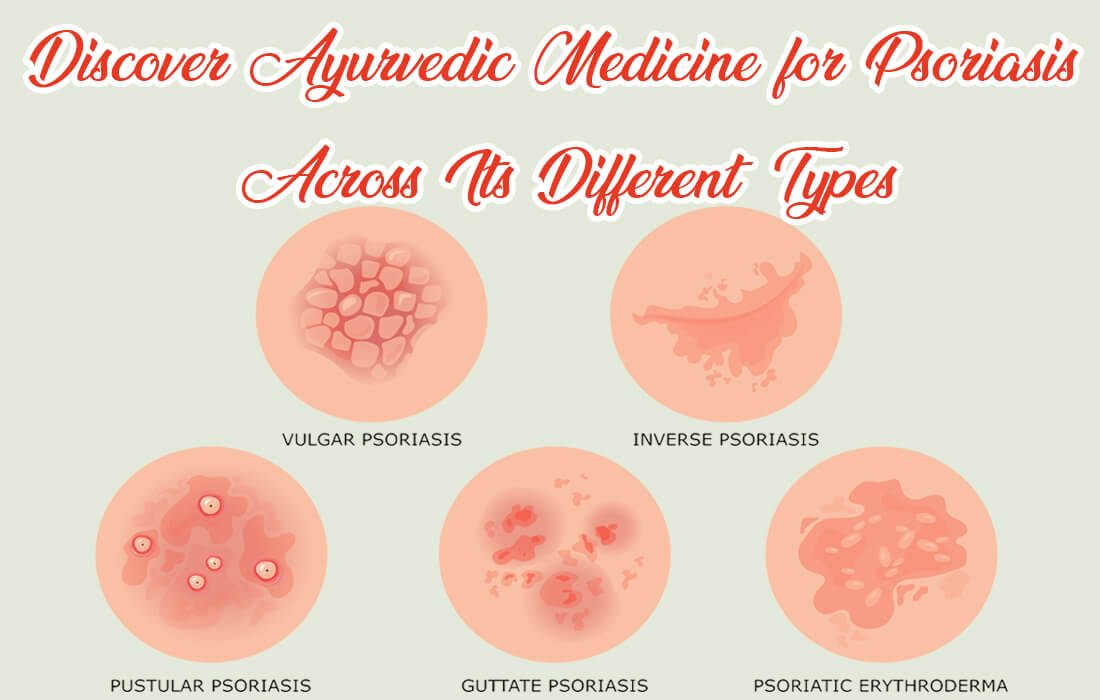
Different Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis, an enduring autoimmune skin disorder, appears in diverse forms, each with unique traits and affected body areas. Understanding the different types of psoriasis is crucial for proper diagnosis and psoriasis treatment in ayurvedic approach. Here, we’ll explain each type of psoriasis:
1. Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris):
- Of all psoriasis cases, plaque psoriasis is the most common, making up approximately 80%. It is characterized by the development of thick, raised, and inflamed patches of skin, often covered with silvery-white scales.
- Plaque psoriasis typically appears on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and also sometimes the face.
- The affected skin can be both itchy and painful. Excessive scratching may result in bleeding and the worsening of symptoms.
- Factors like both stress and infections can trigger or exacerbate plaque psoriasis.
2. Guttate Psoriasis:
- Guttate psoriasis often develops suddenly and is more common in children and young adults. It appears as small, drop-like, pink or red spots on the skin.
- Guttate psoriasis can affect any body part but often starts on the trunk, arms, and legs.
- Streptococcal infections, such as strep throat, commonly trigger guttate psoriasis. Other triggers may include respiratory infections, stress, and skin injuries.
3. Inverse Psoriasis (Intertriginous Psoriasis):
- Inverse psoriasis impacts skin regions with folds, including the armpits, groin, under the breasts, genital and also the buttock areas.
- It affects the Skin folds and creases.
- Unlike other types, inverse psoriasis appears as smooth, red, and inflamed patches without scales. Friction and sweating can worsen the condition.
4. Pustular Psoriasis:
- Pustular psoriasis is characterized by forming small, white, pus-filled blisters (pustules) surrounded by red skin.
- Pustular psoriasis can occur in localized areas or affect large body portions.
- There are two main types: localized pustular psoriasis, which affects specific areas, and generalized pustular psoriasis, which covers a larger portion of the body.
- Pustular psoriasis can be painful, accompanied by fever, chills, and fatigue.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis:
- Erythrodermic psoriasis is a severe and rare psoriasis that can affect the entire body. It results in widespread redness, inflammation, and peeling of the skin.
- This type can cover the entire body surface.
- Skin shedding and severe itching are common.
- Uncontrolled plaque psoriasis, or withdrawal from certain systemic treatments can trigger erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Neglecting ayurvedic medicine for psoriasis could result in a risky situation.
6. Nail Psoriasis:
- Nail psoriasis primarily affects the fingernails and toenails. It can cause changes in the nails, including pitting (small dents or depressions), discolouration, thickening, and nail detachment.
- This psoriasis type concentrates its effects on the fingernails and toenails.
- Nail psoriasis can be painful and lead to discomfort and difficulty using the affected fingers or toes.
7. Scalp Psoriasis:
- Scalp psoriasis occurs on the scalp and can extend to the forehead, neck, and behind the ears. It often appears as red, itchy, and scaly patches.
- It affects both the scalp and hairline areas.
- The scalp is experiencing symptoms such as scaling, itching, and redness. Flakes of skin may fall onto the shoulders.
How to Stop Psoriasis from Spreading
Stopping psoriasis from spreading is a key concern for individuals with this chronic skin condition. You can implement several strategies to prevent the spread of psoriasis lesions and manage the condition effectively with ayurvedic medicine for psoriasis. Here’s a look at how to stop psoriasis from spreading:
Moisturize Regularly:
- Dry skin can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. Keeping your skin well-moisturized can help prevent dryness, reduce itching, and minimize the appearance of scales.
- Choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers and apply them liberally after bathing and throughout the day, especially to affected areas.
Avoid Triggers:
- Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your psoriasis. Common triggers include stress, medications (like beta-blockers and lithium), infections, alcohol, and smoking.
Protect Your Skin:
- Be gentle with your skin. Avoid harsh soaps, hot showers, and aggressive scrubbing, as these can irritate and worsen psoriasis.
- Use mild, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic skincare products suitable for sensitive skin.
Practice Good Hygiene:
- Proper hygiene can help prevent skin infections, which can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
- Keep your nails trimmed to prevent scratching and injury to the skin.
- Maintain clean and dry skin folds, especially in areas prone to inverse psoriasis, to minimize friction and moisture build-up.
Sun Exposure:
- Limited sun exposure can be beneficial for some individuals with psoriasis. Natural sunlight can help reduce symptoms, possibly due to its effects on slowing skin cell growth.
- However, sunscreen or wearing protective clothing is essential to protect your skin from excessive UV radiation.
Stress Management:
- Managing stress is crucial, as it’s a recognized trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and also mindfulness can effectively reduce stress levels.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Adopting healthier lifestyle habits encompasses maintaining a balanced diet filled with natural fruits and vegetables, staying well-hydrated, and also committing to regular exercise. These habits can promote overall skin health and immune system function.
- Stopping psoriasis from spreading involves a combination of effective skincare, lifestyle modifications, stress management, and the best medicine for psoriasis in the Ayurveda Following these methods is essential to manage psoriasis and effectively minimize its impact on your life.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex skin condition that comes in various forms, each with its symptoms and challenges. A better quality of life awaits those with psoriasis as they understand their specific type and embrace effective management strategies. These strategies include both proper hygiene practices and lifestyle modifications. Additionally, ayurvedic medicine for psoriasis offers a natural way to complement conventional treatments.
Early intervention, proper skin care, and stress management are essential to stop psoriasis from spreading. By adopting a holistic approach to treating psoriasis, individuals can effectively manage this condition and minimize its impact on their lives. Remember, psoriasis management is an ongoing process, and with the right approach, you can achieve both relief and improved skin health.