Diabetes, a chronic disorder, afflicts numerous individuals. It involves elevated blood sugar (glucose) levels and can result in significant health issues when not addressed. Unfortunately, many people may not be aware that they have diabetes until it has progressed to a more severe stage. To help prevent this, it’s important to recognize the early signs of diabetes. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the most common causes and symptoms of diabetes, along with the best medicine for diabetes that you should not ignore. Understanding these indications allows you to actively manage your condition and protect your overall health and well-being.
What is Diabetes?
A chronic metabolic condition involves high glucose (blood sugar) levels. The pancreas produces insulin, which is instrumental in managing glucose, a crucial source of energy. Insulin plays a pivotal role as it functions like a key, enabling glucose to enter cells for either immediate energy consumption or future storage.
Diabetes develops when the pancreas, an organ with the role of producing insulin—a hormone essential for regulating blood sugar levels—either does not have enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or when the body’s cells become resistant to the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). As a result, glucose cannot enter the cells effectively, accumulating sugar in the bloodstream.
Neglecting diabetes management can lead to severe health consequences, including an increased risk of heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, vision impairment, and other complications. It is a condition that necessitates lifelong monitoring and careful attention, lifestyle adjustments, and type 1 diabetes medicine. Insulin therapy is employed to manage blood sugar levels and lower the chance of complications.
Causes of Diabetes:
1. Genetics: Genetics are a major factor in diabetes susceptibility within families. If you have close relatives with diabetes, you are at a higher risk.
2. Autoimmune Response (Type 1 Diabetes): In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system’s mistake results in the assault and subsequent loss of the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune response is believed to result from the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. However, the exact cause remains unclear.
3. Insulin Resistance: Type 2 diabetes mainly arises from insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t react effectively to insulin. Over time, the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to compensate for this resistance. Several factors contribute to insulin resistance, including obesity, physical inactivity, and genetics.
4. Gestational Factors: In pregnancy, gestational diabetes emerges when the body’s insulin production is insufficient to cope with increased hormonal demands. While it typically clears up after giving birth, women who’ve had gestational diabetes have an increased likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes as they age.
5. Unhealthy Lifestyle: A lack of physical activity combined with an unhealthy diet filled with sugary, processed foods can lead to obesity and heighten the likelihood of Type 2 diabetes.
6. Metabolic Syndrome: Several factors, such as high blood pressure, increased triglycerides, reduced HDL cholesterol, and abdominal obesity, can significantly boost the chances of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
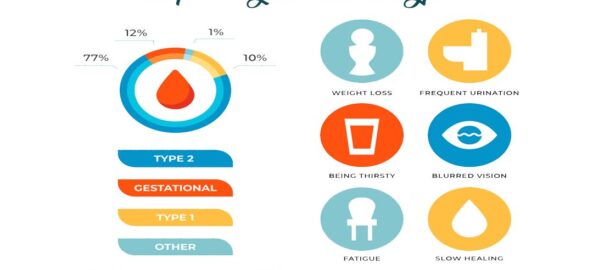
1. Frequent Urination:
High blood sugar forces the kidneys to exert more effort in filtering excess glucose. It leads to more frequent urination, especially at night.
2. Excessive Thirst:
Frequent urination can result in dehydration, causing increased thirst.
3. Weight Loss (Type 1 Diabetes):
In Type 1 diabetes, the body cannot use glucose for energy, so it starts breaking down muscle and fat. It can lead to unintentional weight loss.
4. Fatigue:
Cells are not getting the necessary glucose for energy, leading to persistent tiredness and low energy levels.
5. Blurred Vision:
High blood sugar can change the eye’s lens shape, leading to blurred vision. This symptom is usually temporary and improves once blood sugar levels are controlled.
6. Slow Wound Healing:
Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, making cuts and sores take longer to mend.
7. Frequent Infections:
High blood sugar levels can diminish the immune system’s effectiveness, making one more susceptible to infections such as urinary tract, skin, and gum diseases.
8. Tingling or Numbness (Neuropathy):
Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to tingling, numbness, or pain, often felt in the hands and feet.
9. Increased Hunger:
Despite eating more, you may still feel hungry because your cells are not receiving the glucose they need for energy.
10. Elevated Blood Pressure:
Increased blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, heightening the risk of high blood pressure.
11. Darkened Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans):
This condition may develop in the folds of the skin, such as the neck or armpits, and is often associated with insulin resistance.
12. Sexual Dysfunction: The individual with diabetes may experience sexual problems due to nerve damage and circulatory issues.
13. Complications in Advanced Stages: When diabetes remains poorly managed, it can progress to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney issues, nerve damage, and vision impairment.
One of the most important aspects of managing this disease is monitoring and evaluating a range of symptoms. These symptoms can include changes in blood sugar levels, increases in thirst and urination, weight loss or gain, fatigue, problems with vision, wound healing issues, and frequent yeast infections. It is essential to keep a close eye on these symptoms and consider natural solutions that can be effective, like the medicine for diabetes type 2, if they become particularly severe or persistent.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a condition that can have devastating consequences if left untreated. As we have discussed in this blog post, there are many causes and symptoms of diabetes. Through our exploration of genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors, we have gained valuable insights into the development of this condition and armed you with the knowledge. By paying attention to these early signs and using the best medicine for diabetes, you can take steps to manage this condition and stop its progression. Remember, diabetes is a manageable condition, but it requires effort and dedication on your part. We want to raise awareness about this health issue and encourage individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. Together, let’s work towards a brighter and healthier future.